- Top Page
-
Curriculum
Curriculum
What can be acquired in the
2-year course
Three learning goals
The Clinical Biostatistics Course has three established Diploma Policies, described below. To help students systematically acquire the knowledge, skills, and attitudes required for biostatisticians within two years, its curriculum includes medicine, epidemiology, and research ethics in addition to statistics-related subjects.
-
01
Master the foundation of statistics and biostatistical methodologies that are necessary to ensure the scientific validity of clinical research. Specifically, students must fully understand the ICH E9 "Statistical Principles for Clinical Trials."
-
02
Demonstrate proficiency in biostatistical methodologies through hands-on training in hospitals on statistical analysis, data management, and other activities.
-
03
Acquire the knowledge and attitudes necessary to maintain the ethical integrity of clinical research. Specifically, students must fully acknowledge the Biometric Society of Japan's Standards of Conduct for Statisticians.
Diverse Curriculum
39 credits for students with a non-medical backgdround and
30 credits for students with a medical backgdround are required at least
To complete this course, 33 credits will be required for students with a bachelor's degree in medical fields, and 39 credits for other students. The 33 credits will comprise 10 credits selected from the SPH's five core areas and 4 Task Research credits. Moreover, 19 credits will be required for this course's compulsory subjects: Fundamentals of Statistical Inference, Statisticians' Standards of Conduct, Introduction to Statistical Computing and Data Management, Clinical Trial, Survival Analysis, Statistical Modeling and Applications, Intermediate Biostatistics, Health Data Processing Laboratory, Statistical Methods in Clinical Trials, Data Management for Clinical Research, and Clinical Research Training (Modules I and II). In addition to these 33 credits, students without a bachelor's degree in medical sciences will need to earn an additional 6 credits assigned to Introduction to Clinical Medicine, Basic Medicine I, and Basic Medicine II. This course also offers elective subject credits. For more details, please check the syllabus of the SPH.
A year of Clinical Biostatistics Course
Research activities
Students participate in joint seminars of the Department of Clinical Biostatistics and the Department of Biostatistics every Tuesday. In addition, the HOT Projects are organized every Monday to assist current students in advancing their Task Research and help graduates update their knowledge and receive follow-up. Moreover, the Kyoto Biostatistics Seminar (KBS) is held regularly to discuss statistics, inviting graduates of the Department of Biostatistics and leading statisticians from the research, academic, and industry sectors. Every summer, students majoring in medical/clinical statistics get together and join the Biostatistics Network (BS Network), where students enrolled in this course present their research.
Task Research
The presentation of Task Research is the pinnacle of this two-year course. Students must demonstrate the skills necessary to identify and solve problems and present their work in a way that can be understood by individuals who are not familiar with the research topics. By engaging in their Task Research, students will acquire the planning and presentation skills and the ethical qualities required by biostatisticians who participate in the conduct of clinical trials. Students will present their research results at the joint seminar of the Department of Clinical Biostatistics and the Department of Biostatistics, the annual Biostatistics Network (BS Network), and other academic meetings.
Investigating generalizability of clinical trial results via Cross design synthesis
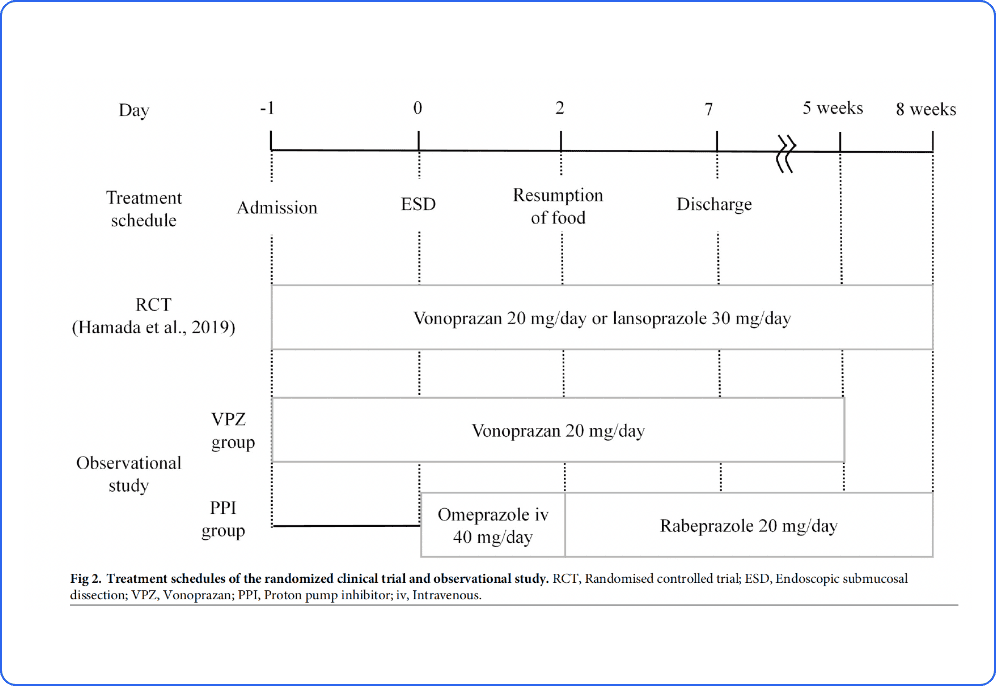
Cross-design synthesis (CDS) is a novel causal inference method for combining data from randomized and observational studies. In this study, pharmaceutical prevention of endoscopic submucosal dissection-induced gastric bleeding was evaluated, adjusting for differences in causal effect estimators in patients who did and did not meet the inclusion criteria of the randomized clinical trial of vonoprazan. The results of the CDS suggested the efficacy of vonoprazan in real-world settings. This study was published in PLOS ONE.
Bayesian statistical model that incorporates similar external data at exploratory clinical trials
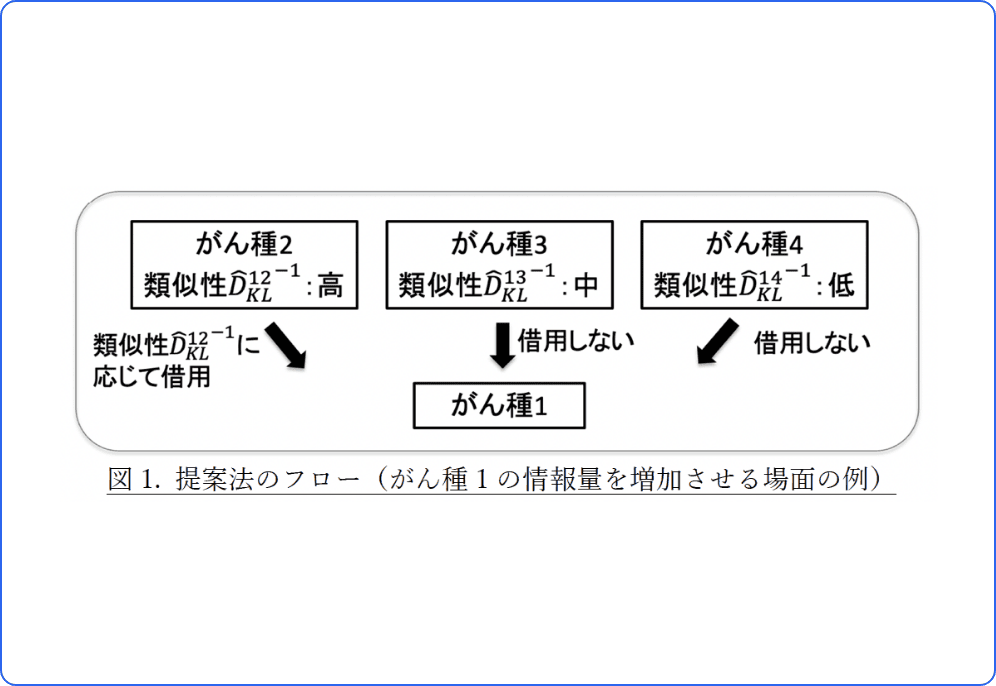
Basket trials are study design for explore the effects of a therapy on a variety of tumors that share the same type of gene mutations, and this novel study design have been of recent interest. This study proposed an information-borrowing approach based on the Kullback-Leibler divergence metric. The results of the simulation showed that gain in statistical power did not lead to a serious inflation of type I error rate. This approach was superior to conventional methods in scenarios where the therapy was effective only for certain limited types of tumors. This study received the Outstanding Student Presentation Award of the Japanese Classification Society.













